
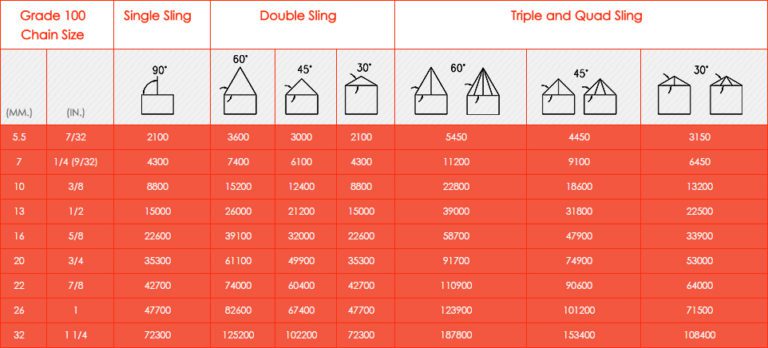
(trainer – explain with the current slings used at your location). capacity sling can safely lift a load at a specific angle using material that weighs 6,000lbs: Important: Remember that the capacity of a sling depends on the type of hitch being used: Choker hitch of a typical 20000lbs rated sling is 9200 lbs. Angle in Degrees from Horizontal Angle Factor 90 1.000 55. This chart will be used as a reference on the following slide. This is used to determine the safe lifting capacity of a sling according to the angle and weight of material being lifted.

(compare this to the slings rating in a choker hitch).Ĥ Sling Angle Chart (if you know the angle of the sling to the lift) This is typically on sling labels. Necessary Rated Capacity of sling = Load Weight x LM = X 1.2 = 7200 lbs. If you don't know the angle: Attach the slings Apply lift until the slings are taut and the load is ALMOST ready to leave the ground (BUT DO NOT LIFT THE LOAD OFF THE GROUND!!) Measure the length of the sling between the lift point and the load Measure the height between the lift point and the load (see below) When you know the actual weight of the load (use material weight sheets), and you need to calculate the appropriate rated capacity (based on the sling angle) of the sling to lift the load, follow the instructions below: (This example uses a measured length of 12 feet and a measured height of 10 feet.) Measured Length (L): 12 feet Measured Height (H): 10 feet Load Multiplier (LM) =L/H=12/10 = 1.2 Load weight: 6000 lbs. This is the angle of concern (the sling to the horizontal lift) on both sides. An angle of thirty degrees should never be exceeded.

Rated capacities are affected by the angle of the lift (sling to load) measured to the horizontal when used with a choker hitch. Highest Capacity (strongest) Less Capacity (weaker) Least Capacity (weakest) 45 degrees 90 degrees 30 degrees Remember, as you change the angle of the slings from 90 degrees to 30 degrees the sling capacity decreases. The load capacity of the sling is determined by its weakest component.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
